Objective: Clone the yield QTL in chromosome 2DL identified in Great Plains hard winter wheat association mapping projects
 |
 |
 |
| Co-PI: Mary Guttieri, Research Geneticist, USDA-ARS, Manhattan, KS | Co-PI:Guihua Bai, Research Plant Molecular Geneticist and Director, USDA Central Small Grain Genotyping Center, Manhattan KS | Guorong Zhang, Assistant Professor – Wheat Breeding, Agricultural Research Center, Hays, KS |
Collaborator: Eduard Akhunov, Associate Professor, Department of Plant Pathology, Kansas State University
Background: In the previous TCAP project, within the Yield QTL Validation Panel, the most significant grain yield QTL in the two highest-yielding environments of seven trials was associated with iSelect SNP IWA8562. Across the seven trial environments, within the 14 families in the panel that were variable for the marker, lines with the preferred ‘A’ allele outyielded sister lines with the ‘C’ allele by 7%. Within the replicated Hard Winter Wheat Association Mapping Panel trials grown in Ithaca, NE in 2012 and 2013, genotypes with the ‘A’ allele of IWA8562 outyielded genotypes with the ‘C’ allele by 202 kg/ha (4.7%).
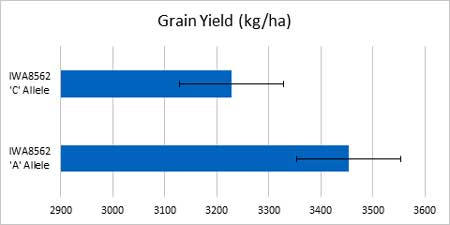 |
| Figure 1. Grain yield of sib selections of fourteen hard winter wheat families variable for the IWA8562 SNP grown in 7 Nebraska environments. The yield difference of 225 kg/ha (7%) was highly significant (p<0.001). |
Recombinant Inbred Mapping Populations: ‘Overland’/’Overley’ and ‘Lyman’/Overley with favorable allele from Overley.
Initial markers: iSelect assays IWA2961, IWA8562 and BS00000905-51 in high LD. The marker haplotypes of Overland, Lyman, and Overley represent landmark regional founder genotypes, ‘Kharkof’, ‘Cheyenne’, and ‘Jagger’, respectively.
Approach: Near isogenic lines carrying residual heterozygosity at the yield QTL locus will be used to develop populations for fine mapping. Recombinants in the target region will be identified by genotyping a large population using the flanking markers followed seed increase for yield testing. Seed will be increased of advanced inbred generations of the mapping populations. In the course of these seed increases, yield components will be evaluated in an effort to identify the basis of the grain yield QTL.
